In today’s digital age, images play a critical role in communication, marketing, design, and education. Among the two major types of digital images—raster and vector—raster graphics are the most commonly used. Whether you’re browsing the web, editing photos, or designing a website, understanding raster images can help you make better visual choices. In this article, we’ll dive deep into what raster graphics are, how they work, and why they matter.
What is a Raster?
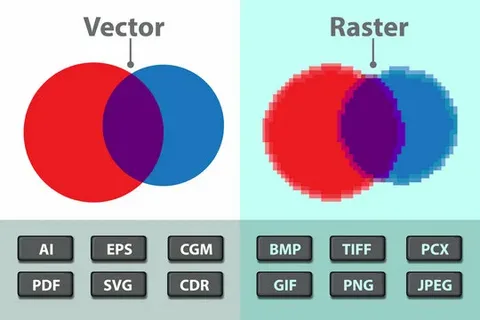
A raster is a type of digital image made up of a grid of tiny rectangular pixels. Each pixel represents a single point of color in the image. When combined, these pixels create a full picture. Raster images are also known as bitmap images, and they are widely used in photography, digital art, and web design.
Common Raster File Formats
Raster graphics come in a variety of formats, each with its own purpose. Some of the most common raster file types include:
- JPEG (JPG) – Ideal for photographs and images with many colors. Offers good compression but can lose quality.
- PNG – Supports transparency and is great for web graphics. It uses lossless compression.
- GIF – Limited to 256 colors but supports animation.
- BMP – A raw bitmap format, often uncompressed and large in size.
- TIFF – High-quality images used in printing and professional photography.
How Raster Graphics Work
Raster images are defined by the number of pixels they contain, also known as resolution. A higher resolution means more pixels and therefore more detail. Resolution is typically measured in PPI (pixels per inch) or DPI (dots per inch) for printing purposes.
For example, a 1920×1080 raster image contains 1920 pixels horizontally and 1080 pixels vertically. When zoomed in or scaled up, raster images can become pixelated or blurry because they rely on a fixed number of pixels.
Advantages of Raster Graphics
Raster graphics offer several benefits:
- Rich Detail and Color: Raster images can display millions of colors and complex gradients, making them ideal for photographs and realistic images.
- Widespread Compatibility: Most software and web browsers support raster formats, making them easy to use and share.
- Ease of Editing: With tools like Adobe Photoshop or GIMP, users can easily edit and manipulate raster images down to the pixel level.
Limitations of Raster Images
While raster graphics are versatile, they also have some limitations:
- Scalability: Unlike vector graphics, raster images don’t scale well. Enlarging a raster image can result in a loss of quality.
- File Size: High-resolution raster images can be large in size, which may slow down web pages and increase load times.
- Compression Artifacts: Formats like JPEG use lossy compression, which can degrade image quality over time if repeatedly edited and saved.
Raster vs. Vector: What’s the Difference?
Understanding the difference between raster and vector images is essential for designers and developers. While raster images are pixel-based, vector images are made up of paths defined by mathematical equations. This allows vector images to scale without losing quality.
Use raster images for rich, detailed visuals like photos. Use vector images for logos, icons, and illustrations that need to scale.
When to Use Raster Graphics
Here are some common scenarios where raster images are the best choice:
- Photographs – Whether for personal use or professional photography, raster is the go-to format.
- Web Design – Raster images are used for web banners, backgrounds, and image content.
- Digital Art – Many digital painting and drawing tools rely on raster graphics.
- Social Media – Most image content on social platforms like Instagram or Facebook is raster-based.
Tips for Optimizing Raster Graphics for SEO
To ensure your raster images contribute positively to your website’s SEO, follow these best practices:
- Compress Images: Use tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim to reduce file size without sacrificing quality.
- Use Descriptive Filenames: Name your files with keywords (e.g., raster-graphic-example.jpg).
- Add Alt Text: Always include relevant alt text to help search engines understand your images.
- Choose the Right Format: Use JPEGs for photos and PNGs for transparent images.
- Responsive Images: Serve appropriately sized images for different screen sizes to improve loading speed.
Conclusion
Raster graphics are a fundamental part of the digital world. From social media to websites and photo editing, raster images provide the detail and color depth that bring visuals to life. Understanding how raster images work—and how to optimize them—can greatly enhance your visual content and improve user experience. Whether you’re a designer, marketer, or casual user, mastering the basics of raster graphics is a valuable skill.